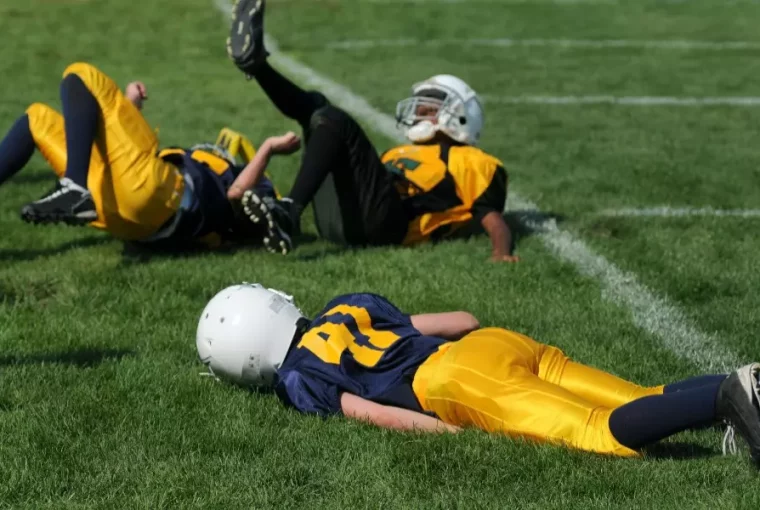
Injuries might feel like a cruel twist of fate to anybody active and healthy. However, to deal with the stress of an injury, you need to have both physical and mental toughness. Los Angeles, California; Miami, Florida; Fort Collins, Colorado, no matter wherever you are from, you can see sports-related injuries are quite common.
While physical rehabilitation is an important part of sports injury recovery, sports psychology practices are essential to mental healing. That is because athletes might feel various emotions, including denial, rage, despair, and even depression after suffering an injury.
This is a serious setback, and you must discover ways to deal with it more constructively. Injuries may assist an athlete to become more focused, flexible, and resilient if they are dealt with graciously.
Top Sports In The U.S.
American football, Baseball/Softball, Basketball, Ice hockey, and Soccer are some of the most popular sports in the U.S. Though they might vary between states.
In Kansas, basketball tops the popularity list. Football, baseball, arena football, hockey, soccer, and wrestling are popular in Oklahoma. Baseball tops the list in Arizona. Baseball is the most popular in Colorado, whether in Denver or Fort Collins.
Sports Injuries Statistics
Organized sports participation in the United States reaches 30 million children and teenagers. More than 3.5 million injuries occur every year, resulting in time off from activity. Sports-related injuries account for a third of all youth injuries.
There are an estimated 3.5 million injuries to children under 14 yearly related to sports or other leisure activities. The major cause of mortality from a sports-related injury is brain damage, which is uncommon. Approximately 21% of all traumatic brain injuries among children in the United States are caused by sports and leisure activities.
Biking, skateboarding, and skating are accountable for half of all sports- and recreation-related head injuries. Emergency departments treat more than 775,000 children under 14 for injuries sustained while participating in organized sports every year.
| Sport | Total Injury | Age: 5-24 | Age: 25 and onwards |
| Track and field activities | 10071 | 8383 | 1687 |
| Bicycles and accessories | 425910 | 188951 | 236958 |
| Swimming | 129708 | 82832 | 46875 |
| Soccer | 81452 | 68123 | 13329 |
| Baseball | 70209 | 48928 | 21281 |
| Basketball | 214847 | 168556 | 46290 |
However, the ratios might vary from state to state. For example, let us consider Los Angeles, California, Miami, Florida, and Fort Collins, Colorado; L.A. has the highest rate of injuries. In comparison, Fort Collins has the lowest injury rate.
That being said, there are many reputable therapy centers near Windsor, Loveland, or Fort Collins, Colorado, for people who are suffering from sports-related injuries. Up And Running Physical Therapy in Fort Collins, Colorado is one of them. This organization helps active adults to overcome injuries such as sports injuries without medications and surgeries. We advise you to treat the following types of injuries seriously and seek professional care if necessary.
Types Of Sports Injuries
Depending on the injury, the symptoms and long-term effects may vary. The following are some of the most common sports injuries:
Achilles Tendon Rupture
It is a strong yet thin tendon located in the ankle’s rear. This tendon is susceptible to rupture during sports. An athlete may face trouble while walking, along with sudden, acute pain with an Achilles tendon rupture.
Sprains
Sprains are caused by overstretching or ripping of the ligaments. Ligaments are bands of connective tissue that hold a bone joint together.
Knee Injuries
A sports injury alters the normal motion of the knee joint. It might be anything from an overstretch to a complete rupture in the knee’s muscles or tissues.
Strains
A sprain occurs when muscles or tendons are overstretched or torn. Bone and muscle are connected by thick, fibrous strands of tissue called a tendon. A widespread misunderstanding is that sprains are the same as strains.
Swollen Muscles
The natural response of a human body to an injury is swelling. As a result, the discomfort and weakness of swollen muscles might be exacerbated.
Dislocations
A sports injury can result in the dislocation of a bone in your body. When this occurs, a bone is forced out of its socket. This can be excruciatingly painful and result in swelling and weakness.
Fractures
Broken bones are another name for fractured bones.
Rotator Cuff Injury
The rotator cuff is made up of four muscles. To move your shoulder in all directions, you need the rotator cuff in place. However, the rotator cuff may be damaged by a tear in any of these muscles.
Diagnosis
Numerous sports-related injuries result in acute pain or discomfort. Others, such as overuse injuries, may not be discovered until long-term harm has occurred. These injuries are often detected during normal physical tests or checkups.
If you believe you have sustained a sports injury, your doctor will most likely perform the following steps to diagnose you. These include the following:
Physical Examination
Your physician may make an effort to reposition the affected joint or body component. This enables them to determine how the region is moving, or not moving, as the case may be.
Medical History
This includes inquiring about:
- how you were hurt,
- what you were doing at the time, and
- what you have done after the injury.
If this is your first appointment with the doctor, they can also request a more detailed medical history.
Imaging Tests
X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (C.T.) scans, and ultrasounds can assist healthcare professionals in viewing your internal injuries. This helps them to diagnose the type of sports injuries.
Coping Strategies
Here are a few strategies to manage during and after injury procedures.
Set Appropriate Goals
Being injured does not exclude you from planning or making goals. Rather than seeing the injury as a setback, embrace it as another training opportunity. Your objectives will now be recovery-oriented rather than performance-oriented. This will assist you to remain motivated.
By tracking your progress toward your objectives, you will be able to detect modest improvements in your injury’s rehabilitation. As a result, you will have a greater sense of assurance that you are progressing.
Bear in mind that you should work closely with your therapist or physician. They can assist you in developing realistic objectives that are appropriate for each stage of your rehabilitation. Most athletes attempt to accelerate their recovery by doing too much too quickly. It is important to recognize that you are wounded and understand your limitations.
Imagery And Psychological Training
When athletes get injured, they are confronted with psychological and emotional issues, which might overwhelm them due to internal and external losses. With the damaging effect that injury may have on an athlete’s psychology, what can they do to maintain a positive mind?
Psychotherapies have been demonstrated to aid athletes in recovering more rapidly from injuries, experiencing more pleasant mood states throughout recovery, and maintaining confidence. Certain programs emphasized the importance of retaining confidence and fostering resilience.
In some research, visualization was the primary tool utilized. However, a study has shown that imagery is a versatile and beneficial tool for developing and maintaining self-confidence.
Previously, imagery therapies were associated with increased recovery times. Although psychologists do not fully understand how imaging works, the mind-body link is probably aided by forming a mental performance blueprint.
According to several studies, the topic of the imaging sessions should entail the athlete seeing themselves managing challenging conditions and overcoming hurdles. Imagining a positive outcome is important because it promotes self-confidence, in the same way completing tangible objectives does.
Emotional Support
According to some sportsmen, family and friends play a critical role in dealing with long-term injuries. They assert that family members and teammates have a significant part in the emotional side of injury recovery.
The social support offered to athletes has a significant impact on how they try to deal with and facilitate an athlete’s return to play. The coach, physiotherapist, teammates, friends, and family of the injured athlete play a major role in facilitating rehabilitation.
Additionally, strong social support from coaches is essential with a combined effort to maintain close and regular personal contact with the athlete and an active interest in the athlete’s rehabilitation.
Rehab
A rehabilitation program might assist athletes in maintaining their fitness level while healing. If rehabilitation is included in your treatment plan, it may involve physical and manual therapy, ultrasonography, or other forms of technology to assist in pain relief and recovery.
Preventing Reinjury
After recovery, you may need additional protective clothing to safeguard an injured body part. This may include customized shoes, tape, or a sports brace to support additional cushioning to guard against a direct strike.
Warm-up before practice and games to help avoid reinjury. Take it easy when you return to your sport and gradually work your way back to your pre-injury level.
Understand your limitations. Examine your body. If a region that has been previously damaged starts to hurt, immediately stop and rest. Pain is your body’s method of communicating something wrong.
Maintaining Fitness While Injured
Depending on the severity of your injury, you may be able to adapt your training regimen or include different kinds of exercise to maintain cardiovascular fitness and strength. Establish an effective alternative fitness regimen by collaborating with your trainer, therapist, or physician. For example, if you cannot run, you may bike or swim.
Additionally, work on relaxation training and flexibility. Develop a modified strength training program, engage in moderate exercise to preserve cardiovascular fitness, or improve nutritional health.
Conclusion
Athletes of all levels are likely to suffer from some injury at some time. Preparedness for physical, emotional, financial, and other setbacks may ease the healing process. It is impossible to know what challenges we will encounter in advance. On the other hand, your finest effort is always appreciated, no matter where you are. Good Luck!